BaaS - Binding as a Service
BaaS is a tool that helps you implement a web service composition framework. One important step in dynamic web service composition is the binding of concrete web services to the activities involved in the composition. BaaS provides this functionality as a service.
Service binding is a complex task, which poses some significant challenges. For each task in the abstract composition model associated with a composite service, there are usually several web services offering the required functionality. However, they may differ in non-functional properties such as reliability, cost, or response time. Therefore, the quality of service (QoS) is the deciding factor in choosing which concrete web service to bind to each task.
In order to make a qualitative comparison of service compositions, it is necessary to estimate the QoS of a composite service based on the QoS of its component services. For this purpose, BaaS uses the QoS extension for BPStruct, which can compute the aggregated QoS values for composite services with complex structures.
Comparing composite services characterized by multiple QoS attributes is not a trivial task, because there is usually no solution that simultaneously optimizes all attributes. BaaS allows its clients to express trade-offs between different QoS parameters, by using the QoSPref approach.
A presentation of BaaS can be found in this paper.
System Requirements
- Windows XP/Vista/7/8
- a 32 bit JRE or JDK installation. (You need a 32-bit installation even on a 64-bit machine. BaaS uses the QoS4BPStruct library, which loads a native library compiled only for 32-bit Windows platforms.)
Installation
Download and unzip the binaries. This will create a directory called baas-1.0, which we will refer to as <BAAS_HOME>.
Open the file <BAAS_HOME>\bin\_settings.bat in a text editor and:
- edit
JAVA_HOMEto point to your 32-bit java installation directory. - edit
BAAS_PORT, if you are not happy with the default value (9090) of the port used by the BaaS server.
Quick start
Open a command line window, go to the directory <BAAS_HOME>\bin and type:
startBaas
Open another command line window, go to the directory <BAAS_HOME>\bin and type:
client ..\config\test1.properties
Congratulations! You have successfully sent a binding request to the BaaS server.
Now it's time to take a closer look at the scripts in the <BAAS_HOME>\bin directory.
startBaaS.bat
Starts the Baas server on the port configured in _settings.bat.
Assuming that the default port 9090 is used, the service will be available at http://localhost:9090/baas.
client.bat
Sends a binding request to the BaaS server. It takes as argument the path to a configuration file containing the following information about the request to be sent:
- the list of QoS attributes (name and aggregation type)
- the QoS constraints
- the QoS preferences
- for each task in the abstract composition model, the QoS values of the concrete web services offering the required functionality
- the abstract composition model
Usage example:
client ..\config\test1.properties
In the configuration file, the abstract composition model is specified by means of two properties:
- the path to a file from which the abstract composition model can be extracted
- the format of the data contained in this file
Two formats are currently supported: xml and bpmn.
The xml format is a BaaS-specific representation of the abstract composition model.
The bpmn format is a business process representation conforming to the OMG specifications.
The file ..\config\test1.properties in the usage example above specifies an xml representation of the abstract composition model.
You can experiment with a bpmn format by opening the file <BAAS_HOME>\config\test1.properties in a text editor and replacing the lines:
workflow.path = ../example/example1.xmlwith the lines:
workflow.type = xml
workflow.path = ../example/example1.bpmn
workflow.type = bpmn
performanceClient.bat
Generates and sends a batch of binding requests to the BaaS server. It takes two arguments:
- the path to a directory containing workflows (abstract composition models in the
xmlformat) - the path to a configuration file controlling the generation of binding requests
- the list of QoS attributes (name and aggregation type)
- the QoS constraints
- the QoS preferences
- the range of component services to be generated for each task of an abstract composition model
- the range of values for each QoS attribute
Usage example:
performanceClient ..\workflows ..\config\perftest1\config.properties
performanceTest.bat
Generates a batch of binding requests for which the best solution is computed. Instead of sending the requests to the BaaS server, it directly calls the solver. The script takes two arguments:
- the path to a directory containing workflows (abstract composition models in the
xmlformat) - the path to a configuration directory
The configuration directory must contain three files:
config.properties, having the same structure as the configuration file needed by theperformanceClientscriptrun.properties, used to configure the number of runs for each workflow and the parameters of the solverlogback.xml, used to configure the logging settings
Usage example:
performanceTest ..\workflows ..\config\perftest1
oryxModelToWorkflow.bat
Converts files from the bpmn format to the BaaS-specific xml format. Several bpmn models created with the Oryx Editor are provided in the directory <BAAS_HOME>\models\oryx. The script takes two arguments:
- the path to a directory containing files in the
bpmnformat - the directory in which the converted workflows should be stored
Usage example:
oryxModelToWorkflow ..\models\oryx ..\tmp-workflows
bitModelToWorkflow.bat
Converts files in the XML format used by IBM WebSphere Business Modeler to the BaaS-specific xml format. Several files in this format taken from the IBM Bit process library are provided in the directory <BAAS_HOME>\models\bit. The script takes two arguments:
- the path to a directory containing files in the XML format used by IBM WebSphere Business Modeler
- the directory in which the converted workflows should be stored
Usage example:
bitModelToWorkflow ..\models\bit ..\tmp-workflows
workflowPicker.bat
From the workflows available in a given directory, selects those being sound and (optionally) satisfying some constraints related to the number of tasks in the abstract composition model.The script takes the following arguments:
-inputDir <path>: the path to a directory containing workflows in the BaaS-specificxmlformat-outputDir <path>: the directory in which the selected workflows should be stored-minTaskCount <number>(optional argument): the minimum number of tasks of the selected workflows-maxTaskCount <number>(optional argument): the maximum number of tasks of the selected workflows
Usage example:
workflowPicker -inputDir ..\tmp-workflows -outputDir ..\picked-workflows -minTaskCount 5
Building BaaS from sources
-
The BaaS source code is managed with Git. If not already available, install git from here.
Open a command line window, go to a directory of your choice and type:
git clone git://git.code.sf.net/p/baas/code baas
This command will create a directory called
baas, in which it will place a clone of the git repository. In thebaasdirectory you will find a subdirectory calledprojects. From here on, theprojectssubdirectory will be referred as<BAAS_PROJ>. -
If not already available, install a 32 bit JDK. You need a 32-bit JDK even on a 64-bit machine. BaaS uses the QoS4BPStruct library, which loads a native library compiled only for 32-bit Windows platforms.
-
Open
<BAAS_PROJ>\gradlew.envin a text editor and setJAVA_HOMEto point to your 32-bit JDK. -
Edit the value of
baasPortin<BAAS_PROJ>\gradle.properties. -
Open a command line window, go to the
<BAAS_PROJ>directory and type:gradlew assemble
BaaS-specific gradle tasks
Open a command line window, go to the <BAAS_PROJ> directory and type:
gradlew tasks
This will display a list of available gradle tasks. Some of these tasks are BaaS-specific and are shortly presented in the paragraphs below.
runBaaS
Starts the Baas server on http://localhost:9090/baas (port value can be configured in
<BAAS_PROJ>\gradle.properties).Usage example:open a command line window, go to the<BAAS_PROJ>directory and type:gradlew runBaaS
runClient
Starts the client program that sends a binding request to the BaaS server.
Usage example:open a command line window, go to the<BAAS_PROJ>directory and type:gradlew runClient -PconfigFile=src/dist/config/test1.properties
runPerformanceClient
Starts the performance client program that sends a batch of binding requests to the BaaS server.
Usage example:open a command line window, go to the<BAAS_PROJ>directory and type (on a single line):gradlew runPerformanceClient -PworkflowsDir=../experiment/src/dist/workflows -PconfigFile=../experiment/src/dist/config/perftest1/config.propertiesdistZip
Creates the binary distribution zip:
<BAAS_PROJ>\build\distributions\baas-1.0.zipUsage example:open a command line window, go to the<BAAS_PROJ>directory and type:gradlew distZip
Eclipse configuration
-
Install a recent version of Eclipse (Kepler or Juno recommended).
-
Configure your 32-bit JDK as standard JRE for Eclipse:
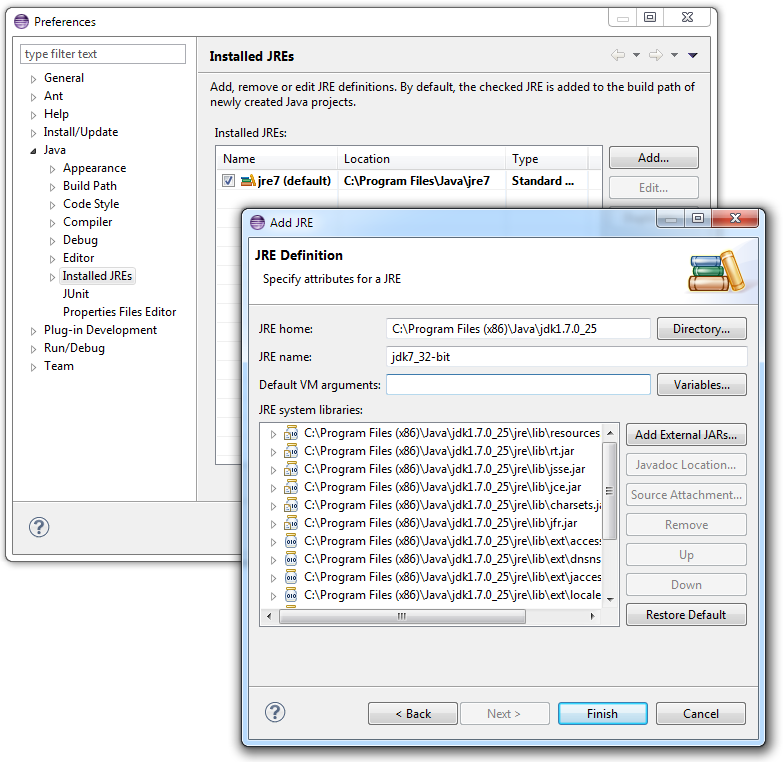
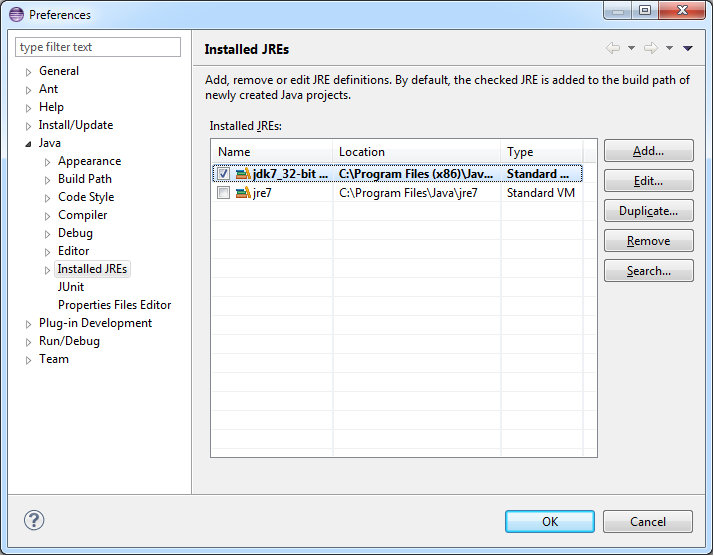
-
Install the
Dynamic Languages Toolkit Coreplugin fromhttp://download.eclipse.org/releases/indigo: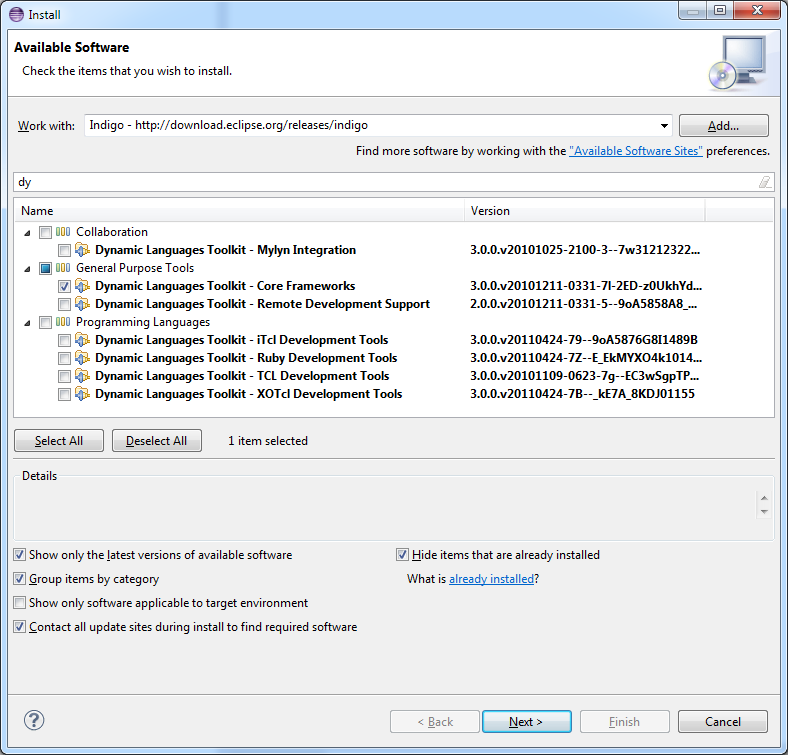
-
Install the ANTLRv3 eclipse plugin from
http://antlrv3ide.sourceforge.net/updates: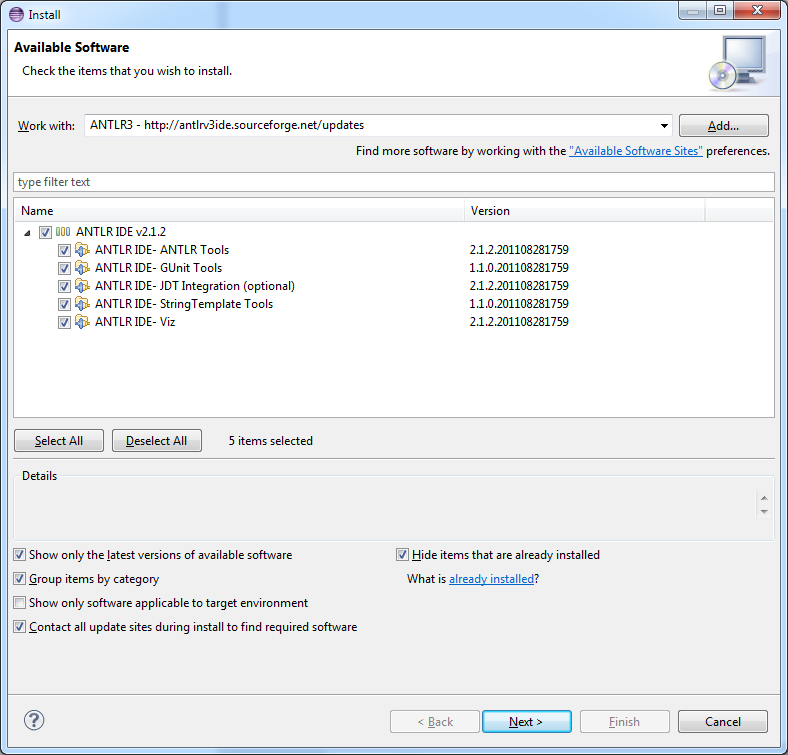
-
If not already available, download and install ANTLRv3.
In Eclipse, configure the ANTLR package as shown in the image below:
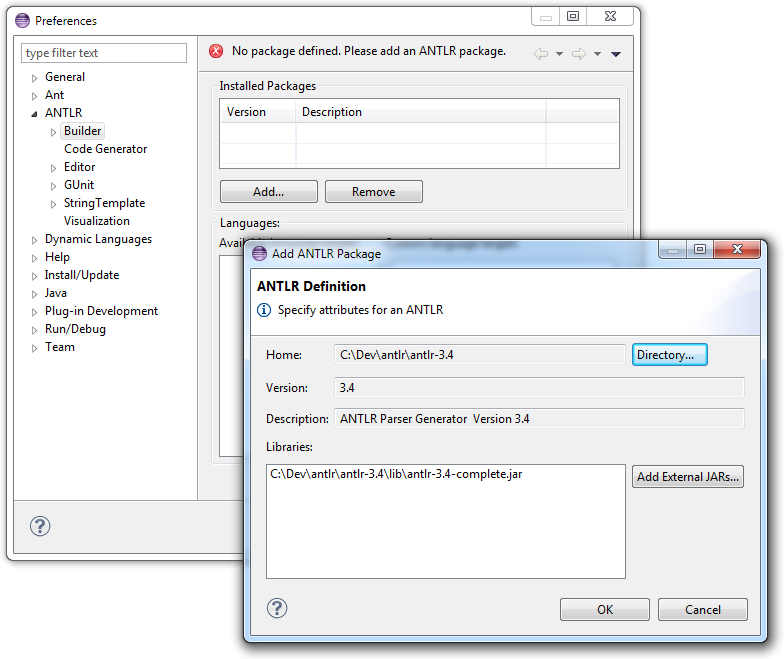
-
In order to generate the Eclipse project files for BaaS, open a command line window, go to the
<BAAS_PROJ>directory and type:gradlew eclipse
-
In Eclipse, import all projects found in the directory
<BAAS_PROJ>
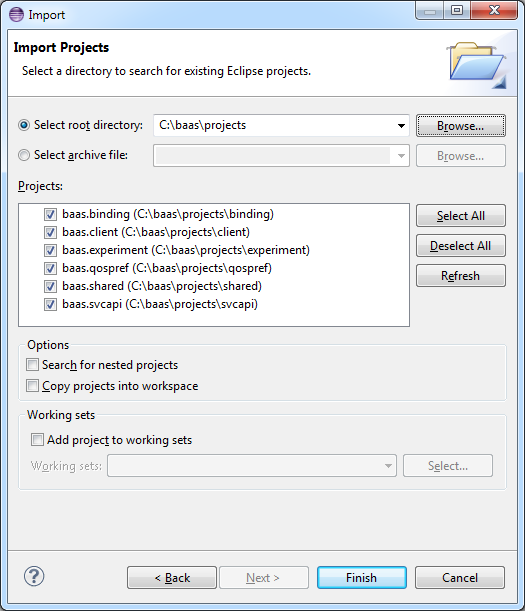
Several launch configurations are already available for the BaaS projects, as seen in the image below:
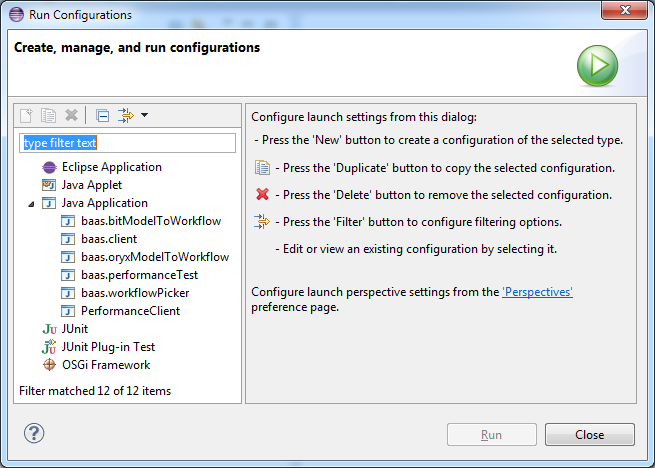
Have fun experimenting with BaaS!